Introduction to Git
• Published on Oct 31, 2019 by zphoenix

Contents
- Git
- Why Git ?
- Installation and Configuration Settings
- Existing project to Git Repository
- Commit
- Clone and Push a repository
- Create a branch for Issues, Push, Merge, Delete a repository after commit
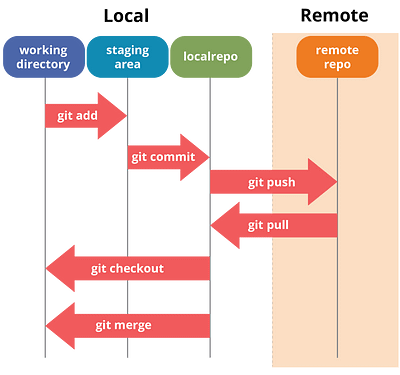
1. Git
Git is a Open-Source distributed control system to manage changes
to source code. It was developed by Linus Torvalds.
2. Why Git?
Most widely used control system in the world. It keeps track of all the
modification to the code. Mistakes or error in source code can be overcome by
looking at the previous changes.
And Git repository hosting service i.e., Gitlab, Mercury, GitHub few more.
3a. Installation
-
GNU/Linux Users
sudo apt-get install git or sudo add-apt-repository ppa:git-core/ppa sudo apt update sudo apt install git -
Windows Users
Download from link : www.git-scm.com/downloads
Select OS and 32bit or 64bit based on your requirement.
3b. Configuration & Production of SSH key
Configuring
git config --global user.name "UserName"
git config --global user.email "UserName@gmail.com"
git config --list
git config --help #For manual page or help page
Production of SSH Key
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
eval $(ssh-agent -s)
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- GNU\Linux User :
xclip -sel clip <~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
- Windows User :
Copy id_rsa.pub content by going to C drive -> User -> UserAccount -> .ssh
4. Existing project to Git Repository
Navigate to project folder from terminal
-
To Git file will be created if the command was executed correctlygit init
-
staging area : The directory we use to organize files that are tracked and committed before pushing it to the repo.git status
-
To add all files & To add a single filegit add -A git add filename
-
To remove all files & To Remove files from staging area :git reset git reset filename
5. Commit
-
To commitgit commit -m “First Commit” #-m is message passed
-
To can view our commitsgit log
6. Clone and Push a repository
To track an existing repo
-
git clone
Example :
mkdir first git clone
ls -la #Shows all files in directory git diff #shows any changes made git add -A git commit -m "Updated first commit"
If several people are working on a single project
-
locations where our repo will get external commit or pushgit remote -v
-
list all git branchesgit branch -a
-
pull changes from remote repogit pull origin master
-
pushes changes to remote repo i.e., master branchgit push origin master
7. Create a branch for Issues, Push, Merge, Delete a repository after commit
Branch :
Usually a developer will create his/her own branch then add things or report.
git branch <branch name>
-
shows all branchesgit branch
-
switches branch<br> <br>git checkout
-
Example : same example… make some changes in file and then
git add -A git commit -m “Update 2”
Push :
-
Origin is the name of and followed by branch namegit push -u origin
git branch -a
Merge :
git checkout master
git pull origin master
git branch --merged
git merge <branch name>
git push origin master
Delete :
git branch --merged
#delete in directory
git branch -d <branch name>
git branch -a
git push origin --delete <branch name>
git branch -a